How to Successfully Adopt ChatGPT in Healthcare: 2025 and Beyond

3 months ago
This is no secret to anyone—how pressurized Canadian healthcare is.
And not just Canada, global healthcare is facing similar challenges.
They want to improve patient care, boost efficiency, and lower costs.
But there is a problem. Doctors spend too much time on administrative tasks.
In Canada, they lose 18.5 million hours a year which is about 55.6 million patient visits.
Villain—the same old methods.
This isn’t just frustrating. It’s costly.
And in all this mess, patient care is compromised the most.
But the good news is, ChatGPT comes as hope in that.
This AI tool has taken the world by storm—reached 100 million users just two months after launch.
- Streamlines workflows
- Cuts down administrative work
- Helps with decision-making
In this blog, we’ll show how healthcare organizations can use ChatGPT to make their operations run smoother and improve care.
Understanding Generative AI and ChatGPT
Generative AI is a type of artificial intelligence that can create new content.
This could be text, images, audio, or even video. Unlike other AI that just analyzes data, generative AI creates new data based on what it’s learned.
ChatGPT is an example of generative AI. This technology is developed by OpenAI, it’s a large language model (LLM) that understands natural language and can generate human-like text.
This makes it useful in many areas, including healthcare.
What ChatGPT Can Do
- It can have realistic conversations.
- It can draft different types of written content like reports and summaries.
- It can even write code and translate languages.
- In healthcare, it can help improve patient care, streamline workflows, and support decision-making. For example, it can create virtual assistants, assist with clinical decisions, generate medical reports, and help educate patients.
What ChatGPT Can’t Do
- Its knowledge is limited to the data it was trained on, which ends in 2021.
- It may not always understand context fully and can show biases from its training data.
- It lacks emotional intelligence and can’t perform physical tasks.
- ChatGPT doesn’t have access to the latest real-time data.
Common Misconceptions
- ChatGPT is not here to replace healthcare professionals. It’s a tool to assist them.
- It’s important not to blindly trust ChatGPT without verifying its information.
- Privacy and data security are big concerns. Using ChatGPT without proper safeguards can expose sensitive health information.
Ethical Use in Healthcare
- Healthcare organizations need to use ChatGPT responsibly and ethically. Patient safety and privacy should always come first.
- Clear guidelines and regulations should govern the use of AI in healthcare.
- For example, when using a third-party chatbot like ChatGPT, ensure they comply with privacy regulations such as HIPAA.

Use Cases of ChatGPT in Healthcare
Let's explore some of the practical applications of ChatGPT which can potentially transform today's healthcare.
1. Patient Communication
Virtual assistants for telemedicine and scheduling:
Telemedicine is a growing practice among patients and doctors, and ChatGPT can add an extra layer of convenience to it.
This AI chatbot can manage appointments and answer common health questions.
According to a 2021 survey by Accenture, 67% of patients faced negative experiences and reason—administrative chaos. ChatGPT can solve this.

Simplifying medical explanations:
Understanding a medical language is not easy. It is full of complex terms and not every patient can get it.
With ChatGPT they can get the explanation in simple words like a diabetes patient can learn about their diagnosis, treatment options, and lifestyle tips in an easy-to-follow way.
Empathy and support:
You don't believe but it's true that most people are using ChatGPT for companionship or emotional support. This application can be harnessed in healthcare too.
ChatGPT technology can craft caring messages for patients during difficult times. Emotions support all that a patient needs in their healing.
2. Medical Documentation
Automating summaries:
ChatGPT can review patient data and generate summaries of interactions or medical histories.
Recently JAMA did a survey and found something unusual. The report says most clinicians spend nearly 2 hours per week on after-hours documentation.
Something doesn’t feel right, does it?
Drafting medical notes:
This is the favorite application of healthcare providers.
It's their dream that someone can write progress notes, treatment plans, and discharge summaries.
Well in that case, ChatGPT is making their dream come true.
3. Medical Research
Summarizing studies and clinical trials:
Analyzing long research papers and finding useful, is a very challenging task. It consumes the researcher's time.
Well, with ChatGPT, you can do it in seconds. It can easily summarize clinical trials on cancer treatments and list effectiveness and side effects.
Finding research gaps:
ChatGPT can highlight the areas which have higher needs for research. This helps researchers focus on unmet needs.
4. Other Applications
- Clinical decision support: ChatGPT can provide real-time recommendations, such as flagging potential drug interactions.
- Mental health support: ChatGPT-powered chatbots can screen for mental health issues, suggest coping strategies, or connect patients with resources.
- Medical training: Medical professionals and students can use ChatGPT to access the latest information and learn faster.
- Remote patient monitoring: ChatGPT can analyze wearable data, like heart rate or sleep patterns, to track patient health and alert providers if needed.

Crafting Effective Prompts for ChatGPT in Healthcare
ChatGPT can revolutionize healthcare tasks, but crafting the right prompts is key to unlocking its potential. Let’s look at how to create clear and effective prompts:
1. Be Specific
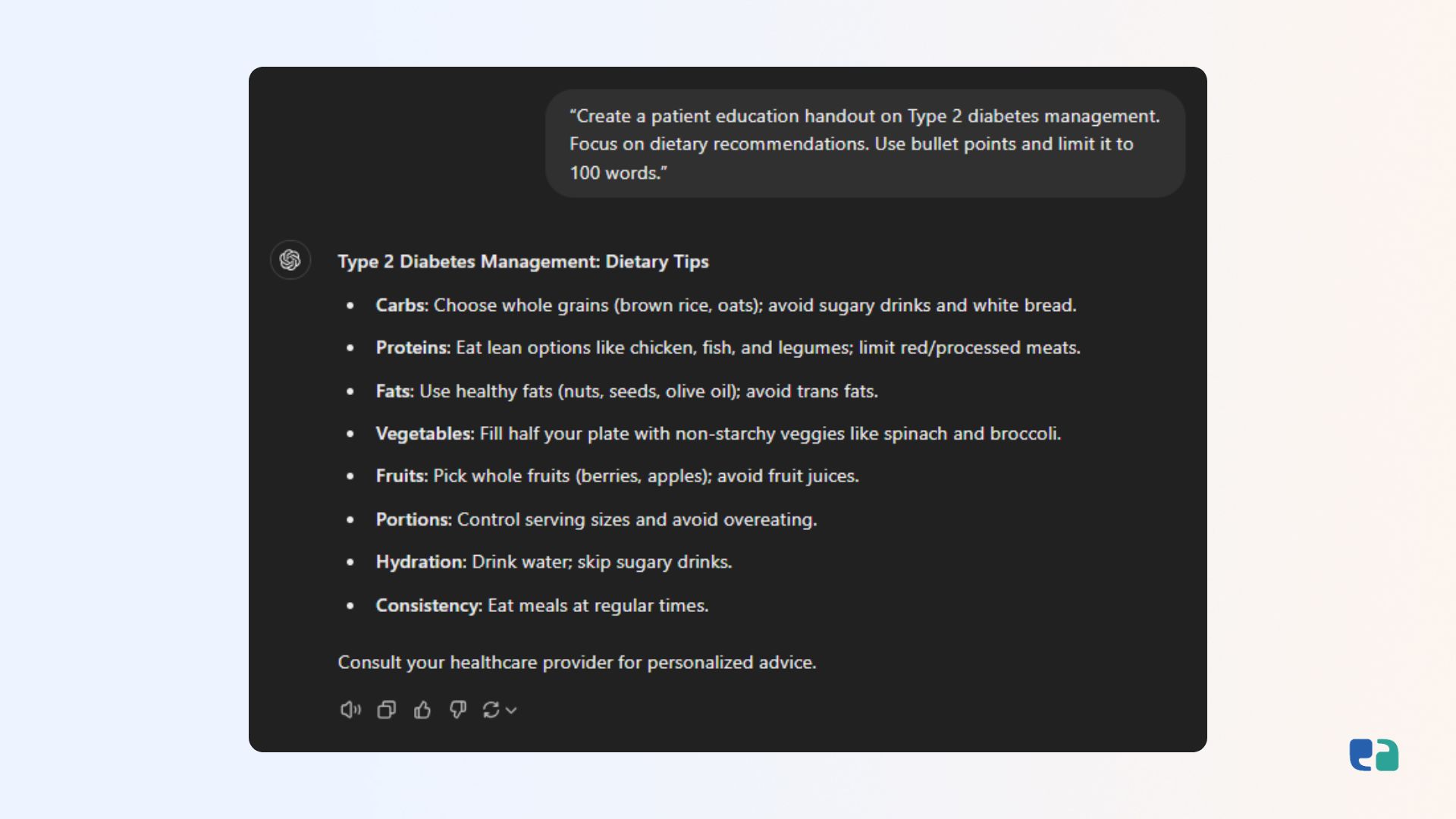
Clear prompts lead to precise responses. Define what you need, including the format, length, and details. For example:
“Create a patient education handout on Type 2 diabetes management. Focus on dietary recommendations. Use bullet points and limit it to 200 words.”
This level of detail ensures ChatGPT understands your expectations.
2. Ask Open-Ended Questions
Instead of yes/no questions, ask for in-depth explanations. For instance:
“Describe how ChatGPT can be used for patient education, providing specific examples of its applications.”
This approach encourages detailed and actionable responses.
3. Keep it Simple
Avoid jargon or overly complex language. ChatGPT performs best when instructions are easy to understand.
4. Provide Context
Context helps ChatGPT deliver relevant answers. For example:
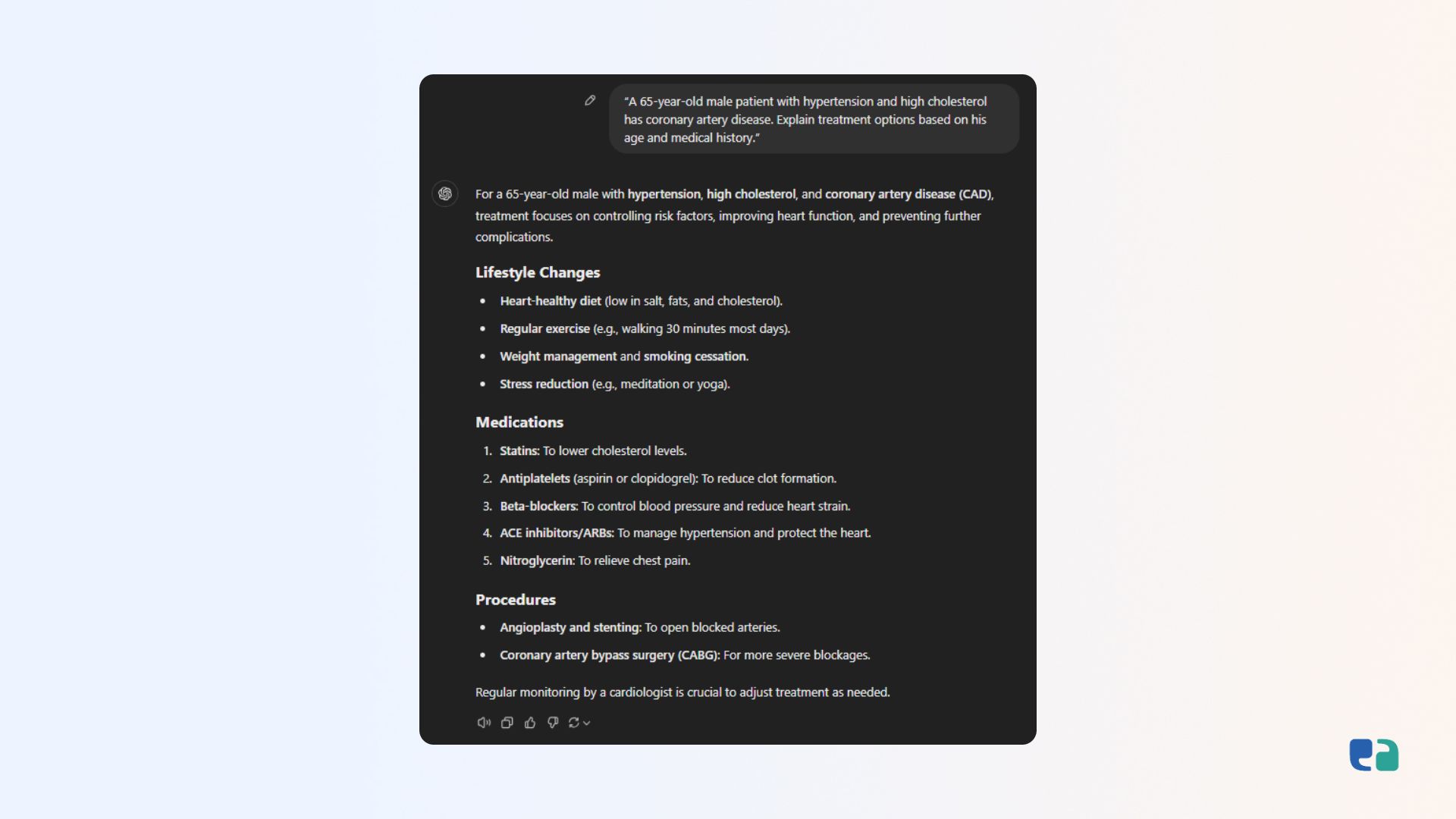
Instead of asking, “Explain the treatment options for heart disease,” give more background:
“A 65-year-old male patient with hypertension and high cholesterol has coronary artery disease. Explain treatment options based on his age and medical history.”
5. Refine Your Prompts
If the response isn’t what you expected, tweak your prompt.
For example: If the answer is too technical, adjust your prompt to request simpler language. Iterating prompts helps achieve the desired output.
Implementation Considerations for Healthcare Organizations
Let's address some important aspects before implementing AI like ChatGPT in your medical practice.
1. Data Privacy and Security
Protecting Patient Data
When it comes to healthcare, following compliance is a must.
Before ChatGPT adoption make sure you follow PIPEDA & HIPAA regulations or as per the country you are operating in.
For example, entering Protected Health Information (PHI) into ChatGPT without a signed Business Associate Agreement (BAA) is a HIPAA violation. While OpenAI encrypts data and removes personal information, they don’t currently sign BAAs.
For more insights on compliance, consult Canadian compliance experts who specialize in the local healthcare landscape.
Keeping Data Secure
- Encryption: Encrypt all data in transit and at rest. This assures if a breach happens, the offender can't read the data.
- Access Control: Restrict data access to authorized staff. Use multi-factor authentication and regularly audit user permissions.
- Breach Response Plan: You should have a clear plan for managing data breaches before embracing ChatGPT.
- Identifying the issue
- Containing it
- Notifying patients & authorities
2. Integration with Existing Systems
Connecting AI with EHRs and Tools
During AI integration in your healthcare system don't forget to standardize data.
Using APIs and FHIR standards can simplify this process. FHIR ensures AI tools communicate effectively with EHRs.
Data Standardization
Well, even AI likes cleanliness.
AI gives an optimal output when input data is clean and consistent. Standardized data format provides better insights with a smooth integration to the system.
If you want to reduce the variability, we suggest you create a plain-language knowledge base from existing EHRs, analytics platforms, and data warehouses.
3. Staff Training and Education
Training Healthcare Staff
Train your staff to use AI tools effectively and responsibly.
- Capabilities and Limitations: Teach staff what AI can and cannot do to set clear expectations.
- Privacy and Security: Ensure staff know how to protect patient data while using AI.
- Ethics: Discuss ethical considerations, such as addressing biases and maintaining human oversight in decisions.
Understanding AI Bias and Accuracy
The AI system is not perfect, it can be biased depending on the data they got during the training.
Staff should learn to identify and question biased outputs. Make sure your staff keeps learning and critically evaluates AI outputs.
4. Ethical Considerations
AI in Patient Care
AI is a trusted technology but not fully. It's good for assistance but there is always a need for clinical monitoring.
Ensuring Fairness and Transparency
- Bias Mitigation: To reduce the biases, use diverse datasets. You should also conduct regular audits.
- Transparency: Explain to patients how AI is used in their care and get informed consent when necessary.
- Accountability: Make sure the roles and responsibilities of AI outcomes are defined. It will help to address the errors.

