The Fundamentals of the Pharmacy Supply Chain

3 months ago
The pharmaceutical industry plays a vital role in ensuring the health and well-being of individuals around the globe.
Behind the scenes is a complex and intricate network of processes and systems, known as
The pharmacy supply chain.
It is responsible for the seamless delivery of medications from prescription to medicine dispensing.
However, this supply chain has its challenges.
Let’s dive deep into the fundamentals of the pharmaceutical supply chain.
Diving Into The Pharmacy Supply Chain
The pharmacy supply chain encompasses the entire journey of medication, starting from its production to the point of patient consumption.
This multifaceted process involves numerous stakeholders, including
- Pharmaceutical manufacturers
- Distributors
- Pharmacists
- Healthcare providers
- Patients
Each step in the supply chain is crucial.
Any inefficiency or disruption in the pharmacy supply chain can have serious consequences on patient health and well-being.
The Pharmacy Supply Chain Stakeholders
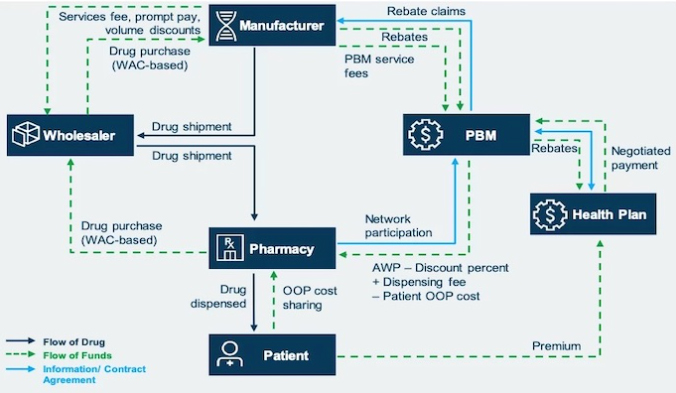
The pharmacy supply chain involves several key stakeholders who play crucial roles in the journey of medications from production to patient consumption.
1. Pharmaceutical Manufacturers
These are the companies responsible for the pharmaceutical products
- Research
- Development
- Production
They ensure that medications are manufactured in compliance with regulatory standards, maintaining quality, safety, and efficacy.
2. Wholesalers (Distributors)
Wholesalers or distributors serve as intermediaries between pharmaceutical manufacturers and other stakeholders in the supply chain.
They purchase medications in bulk from manufacturers and distribute them to various points of sale, such as pharmacies, hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare providers.
3. Pharmacies
Pharmacies, including retail pharmacies and hospital pharmacies, are the primary points of contact between patients and the healthcare system.
Pharmacists play a vital role in
- Dispensing medications
- Providing patient counseling
- Ensuring safe and appropriate medicine use
They also manage inventory and collaborate with other stakeholders to ensure the availability of medications.
4. Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers, including doctors, nurses, and other medical professionals, prescribe medications to patients based on their diagnoses and treatment plans.
They rely on the pharmacy supply chain to ensure that prescribed medications are available for their patients when needed.
5. Patients
Patients are the ultimate beneficiaries of the pharmacy supply chain.
They rely on the pharmaceutical supply chain to access safe and effective medications for their health conditions.
Patients may receive medications directly from pharmacies or through healthcare providers in various settings.
6. Regulatory Authorities
Regulatory authorities, such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States, are responsible for overseeing and regulating the pharmaceutical industry.
They establish and enforce regulations and standards to ensure the safety, efficacy, and quality of medications.
Regulatory authorities also monitor the pharmacy supply chain to prevent the circulation of counterfeit or substandard drugs.
7. Payers/Insurance Companies
Insurance companies and payers play a role in the pharmacy supply chain by facilitating reimbursement and managing medication coverage for patients.
They collaborate with pharmacies, healthcare providers, and pharmaceutical manufacturers to ensure access to medications while managing costs and maintaining compliance with insurance policies.
The Workflow of the Pharmacy Supply Chain
Though the pharmacy supply chain workflow is a bit complex, we will try to make it as simplified as possible for you.
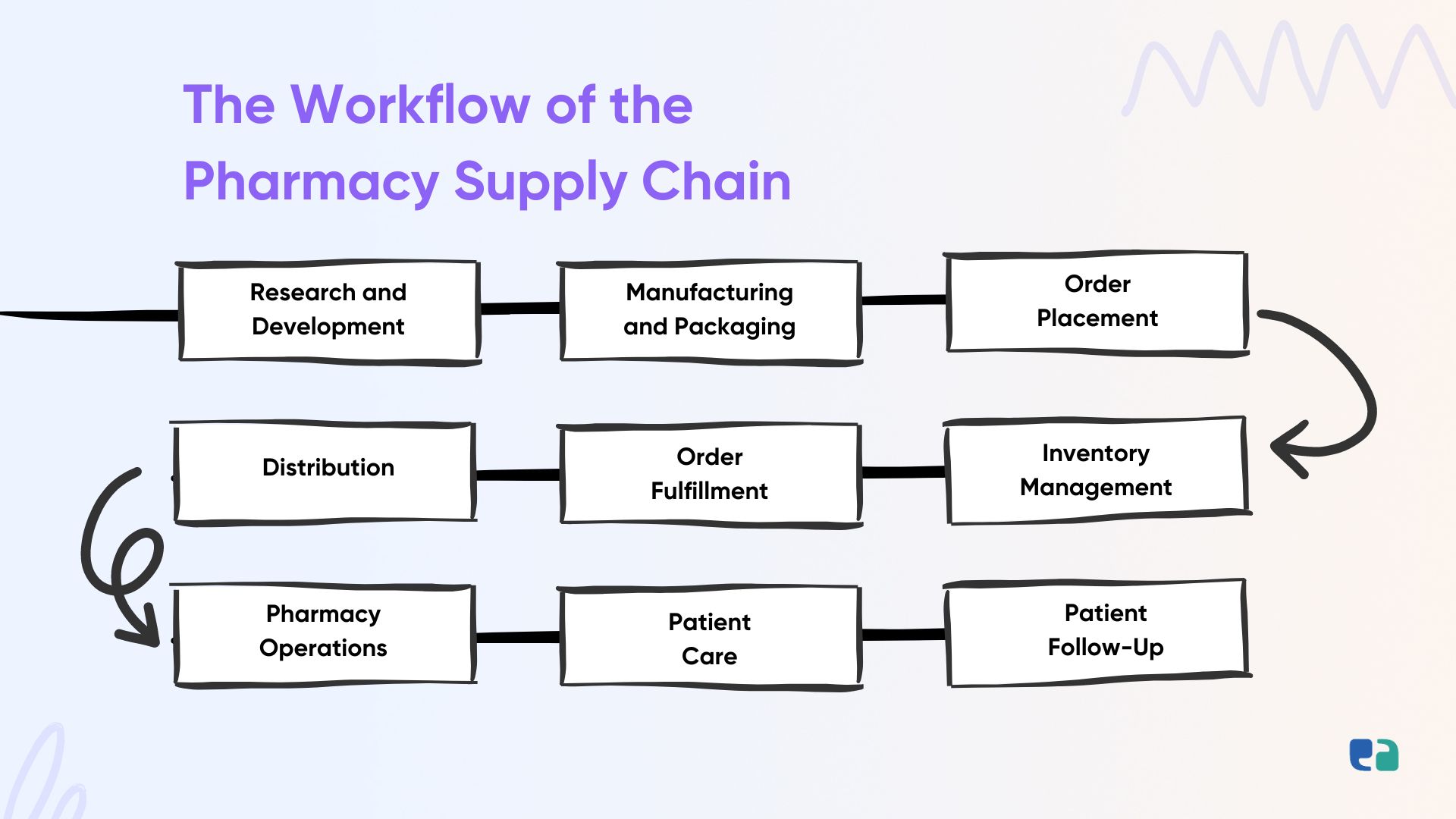
1. Research and Development
Pharmaceutical manufacturers conduct extensive research and development to discover and develop new medications.
This involves preclinical testing, clinical trials, and obtaining regulatory approvals.
2. Manufacturing and Packaging
Once a medication is approved, pharmaceutical manufacturers produce the medication in large quantities.
The manufacturing process involves
- Sourcing raw materials
- Compounding
- Formulation
- Quality control
The medications are then packaged, labeled, and prepared for distribution.
3. Order Placement
Wholesalers or distributors receive orders from
- Pharmacies
- Hospitals
- Other healthcare providers
These orders indicate the medications and quantities required to meet patient needs.
4. Inventory Management
Wholesalers manage their inventory by sourcing medications from pharmaceutical manufacturers and storing them in warehouses.
They must balance stock levels to meet demand while minimizing waste and the risk of medication expiry.
5. Order Fulfillment
Wholesalers retrieve the medications from their inventory and prepare them for shipment.
They package the medications securely, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards and maintaining product integrity.
6. Distribution
Medications are shipped from wholesalers to pharmacies, hospitals, and other healthcare providers.
This involves logistics coordination, including transportation, warehousing, and tracking to ensure timely and secure delivery.
7. Pharmacy Operations
Pharmacies receive the medications from wholesalers and store them appropriately.
Pharmacists and pharmacy staff
- Manage inventory
- Dispense medications
- Provide patient counseling
- Monitor medication adherence
8. Patient Care
Healthcare providers prescribe medications to patients based on their diagnoses and treatment plans.
Patients receive prescriptions and visit pharmacies to obtain their medications.
Pharmacists counsel patients on
- Proper medication use
- Potential side effects
- Any necessary precautions
9. Patient Follow-Up
Pharmacies maintain records of medications dispensed to patients.
It facilitates medication adherence monitoring and follow-up care.
Patients may revisit pharmacies for prescription refills or consultation with pharmacists.
Throughout this workflow, regulatory compliance, quality assurance, and safety measures are essential.
The pharmacy supply chain must adhere to regulatory requirements, such as
- HIPAA
- Quality control standards
- Product serialization
These regulations ensure patient safety and the integrity of medications.
The Challenges in the Pharmacy Supply Chain
1. Product integrity
Ensuring the integrity of pharmaceutical products is of utmost importance.
Counterfeit drugs pose a significant risk to patient safety and can compromise the effectiveness of treatments.
The pharmacy supply chain must implement robust measures to track and authenticate products at every stage.
2. Regulatory Compliance
The pharmaceutical industry is subject to stringent regulations to ensure that medicines are
- Safe
- Efficient
- High-Quality
Compliance with these regulations adds complexity to the supply chain, requiring
3. Inventory Management
Balancing inventory levels to meet fluctuating demand while minimizing waste and expiration of medicines is a perpetual challenge.
Overstocking or understocking can lead to financial losses or medication shortages, potentially impacting patient care.
By accurately forecasting demand, companies can optimize inventory management, reduce waste, and ensure an adequate supply of medications for patients.
4. Traceability and Visibility
Timely access to accurate information regarding the location, status, and condition of pharmaceutical products is critical.
Lack of real-time visibility and traceability can result in
- Delays
- Product recalls
- Compromised patient safety
End-to-end visibility ensures transparency and enables quick response times to potential disruptions, minimizing supply chain risks and enhancing patient safety.
The Forrester Effect on the Pharmaceutical Industry
The Forrester effect is also known as the "bullwhip effect."
It refers to the phenomenon of demand fluctuations amplifying as they move upstream through the supply chain.
This concept was first described by Jay Forrester, an MIT professor, in the 1960s, and it has been observed in various industries, including the pharmaceutical industry.
The Forrester effect describes how even minor variations in consumer demand can lead to significant oscillations and inefficiencies in the supply chain.
These fluctuations can result in challenges such as
- Inventory imbalances
- Excess inventory
- Shortages
- Increased cost
- Medicine availability disruptions
Several factors contribute to the Forrester effect in the pharmaceutical industry.
1. Lack of Real-Time Information
The flow of information across the supply chain may be delayed or distorted, leading to inaccurate demand forecasting.
As a result, downstream stakeholders may overestimate or underestimate demand, leading to inefficiencies in production and inventory management.
2. Batch Ordering
Wholesalers and distributors often place orders with pharmaceutical manufacturers in batches rather than in response to real-time customer demand.
This batching can magnify demand fluctuations as the orders move upstream, creating a mismatch between actual demand and order quantities.
3. Inventory Buffering
Stakeholders in the supply chain often maintain inventory buffers to mitigate the risk of stockouts and meet uncertain demand.
However, these buffers can intensify the Forrester effect.
For example, when downstream retailers or pharmacies increase their inventory levels in response to perceived shortages or demand spikes, it can create a ripple effect of inflated demand forecasts upstream.
4. Variability in Lead Times
Lead times, the time taken for a product to move from one stage to another in the supply chain, varies due to
- Transportation delays
- Regulatory processes
- Other factors
Variability in lead times can further amplify the Forrester effect, as it introduces uncertainty and complicates demand planning.
Companies in the pharmaceutical supply chain need to recognize and address the Forrester effect to
- Optimize their operations
- Minimize disruptions
- Improve overall supply chain performance
Partner with the Best Software Development in Canada to Overcome the Challenges of the Pharmacy Supply Chain
The Forrester effect poses significant challenges to the pharmaceutical industry, creating demand fluctuations that ripple through the supply chain.
However, our innovative solutions can help mitigate these challenges and optimize supply chain operations.
We are a Canadian-based healthcare software development company working in the domain for 8+ years.
Our expertise and experience help us to address the complexities of the pharmacy supply chain.
With the knowledge gained over the years, we offer a range of services and cutting-edge technologies to revolutionize the pharmaceutical supply chain.
We enable transparency, quick response times, and enhanced traceability, reducing the risk of delays, product recalls, and counterfeit drugs by implementing advanced technologies like,
Our supply chain solutions provide end-to-end visibility, allowing stakeholders to track and monitor the movement of pharmaceutical products in real-time.
- RFID
- IoT
- Blockchain
Get in touch with us today and learn more about our innovative solutions.
